Those carp are are worse than most believe and can destroy a complete sports fishery.
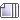
bighead carpAsian carp get really big! This particular Bighead carp is about to be studied by USGS scientists
United States Geological Survey
What are carp?
Carp are a family of fish native to Europe and Asia. The common carp (Cyprinus carpio) has been in the US for over 100 years - long enough that we don't really know what our waters would be like without them. The common carp is considered a nuisance fish, but it doesn't seem to be doing too much harm to the lakes and rivers it lives in.
The newest carp invaders, bighead carp, black carp, grass carp, and silver carp (collectively known as "Asian carp"), seem to be causing trouble in the Mississippi River and surrounding waters.
Introduced to the U.S. in the 1970's to control weed and parasite growth in aquatic farms, Asian carp eventually managed to get into the Mississippi River and establish breeding populations. Asian carp are slowly making their way up the Mississippi River and its tributaries, and have been found as far north as Minnesota.
Why are carp a problem?
Asian carp cause serious damage to the native fish populations in the lakes and rivers that they infest because they out-compete other fish (video, 1 min) for food and space. Carp are also thought to lower water quality, which can kill off sensitive organisms like native freshwater mussels. Asian carp have been known to dominate entire streams (video, 45 sec), effectively pushing out the native species.
Silver carp are known to jump out of the water at high speeds, which can injure boaters and damage boating equipment. So, what does a school of jumping silver carp look like? Check out this documentary: Asian Carp Invasion (video, 7min).
Experts are worried that if these fish get into the Great Lakes, they may negatively affect the area's $7 billion/year fishing industry. By out-competing native fish species for food and habitat, carp may reduce the populations of native fish that are so important to fishermen. Even if Asian carp are kept out of the Great Lakes, continued spread throughout the Mississippi River watershed could result in them reaching 31 states and 40% of the continental United States, spelling disaster for our nation's freshwater ecosystems.
How do carp spread?
Asian carp (especially Silver carp) are capable of jumping over barriers, including low dams. Flooding can spread these fish as well, because flooding can connect water bodies that aren't normally connected. This makes it possible for fish to travel to new areas. Recent floods may have helped the fish spread further.
Asian carp are also spread by human actions. The release of live bait containing young carp has introduced these fish to numerous water bodies. Watercraft that use the Mississippi locks allow carp to move upstream when the locks are opened to allow boats through. Additionally, boats that aren't drained after use can carry young carp or eggs that may be released into the water the next time the boat is used.
Releasing even a few carp into a body of water can become a huge problem. While the adult carp prefer slow moving water, they look for high, fast moving water when laying eggs (a process called spawning). They lay hundreds of thousands of eggs at a time, multiple times per year, which means populations grow and spread quickly. Because of this, they can quickly out-compete native species, and put ecosystems in danger.
What do carp eat?
The grass carp can eat up to 40% of its body weight in plants every day. Other species of carp consume up to 20% of their body weight daily. They can reach a maximum weight of 110 pounds (although the average is closer to 50).
Bighead and silver carp eat plankton, which native mussels and fish depend on. Grass carp consume plants, and can drastically change river and shoreline vegetation. Black carp have human-like molars and eat snails and mussels, including native species that are already endangered.
When the amount of plants, mussels, and plankton are lower in our lakes and rivers, the ecosystem becomes unbalanced and our native species that depend on these food sources suffer.